Choice Based Conjoint (CBC)
USING CHOICE BASED CONJOINT TO CREATE REALISTIC DECISION-MAKING SITUATIONS IN YOUR MARKET RESEARCH ON PRODUCT PREFERENCES
The Choice Based Conjoint (CBC) from the group of Discrete Choice Modelling methods offers a realistic decision situation. The respondent chooses one product of a set of products. However, he also has the option to decide against all products presented, i.e. to explicitly choose none of them. This is very close to a real shelf situation.
Like the Adaptive Conjoint, the Choice Based Conjoint is also preferably computer based. The use of graphical elements is particularly suitable for this method. Additional advantages of this method include its ability to reveal the extent to which attributes have a mutual influence on one another (measurement of interactions). Undesired combinations of attribute levels can be excluded when compiling the stimulus examples.
MISSING INFORMATION IS ESTIMATED IN CHOICE BASED CONJOINT ANALYSIS
Using the so-called Hierarchical Bayes Estimation Method, the missing information is supplied at the individual level based on the structures in the group as a whole. However, this requires that a certain minimum level of homogeneity be present within the group. If this minimum level is not present, subgroups exhibiting similar decision structures can be created in a parallel estimation and segmentation process (Latent Classes Method). Individual utility values can therefore only be determined at the end of the study based on all of the obtained survey data.
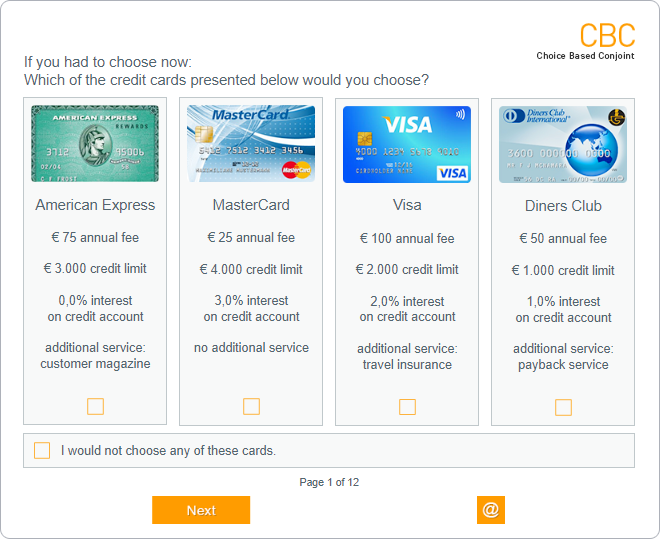
Choice Based Conjoint
NUMEROUS VARIANTS, EXTENSIONS AND ADDITIONAL OPTIONS FOR THE CHOICE BASED CONJOINT METHOD IN THE IFAD PORTFOLIO
- Prohibitions, Conditional Display, Conditional Pricing and Tooltips
– Prohibitions: Mutual exclusions from levels
– Conditional display: display of graphic elements and / or text in dependency on levels of one or more attributes
– Conditional pricing: display of prices depending on levels of one or more attributes taking into account a uniform calculation rule
– Tooltips: Additional information on attributes and levels via mouseover or enlargement will be shown to respondents
- Dual Response None
In some surveys the Standard None Option may be chosen very often. In the context of the evaluation, this leads to more unstable benefit estimates because less data is available for this. When using the Dual Response None, every respondent is asked to select the most preferred concept for each CBC question. A second question is then used to determine whether the person would actually buy the selected alternative. The respondent confirms his selection.
- Purely graphic representation in Choice Based Conjointg
E.g., it is possible to assemble concepts from purely graphic elements.
- Choice Based Conjoint with Alternative Specific Design
One or more attributes are only shown when one or more specific levels of another attribute occur.
- Choice Based Conjoint on Smartphones (mobile CBC))
IfaD offers the best possible optimized display for the survey on smartphones including advice on what works or does not work.
- Individual Choice Based Conjoint programming
If there are special requirements for the presentation of concepts or the sequence of questions, IfaD can implement them flexibly using individual programming.
- Shelf Choice Based Conjoint (Shelf CBC)
A Shelf Conjoint is a special CBC with the attributes product and price plus possibly package size. All products are always shown at the same place on the screen, the price per product varies from screen to screen. The arrangement of the products of the CBC is similar to a shelf and usually a shelf in which the products are arranged is indicated.
- Individualized Choice Based Conjoint
The individualized CBC enables the individual deselection / selection of levels of an attribute if we have a large number of levels that cannot be divided into several attributes with a few levels each (e.g. flavours for jam).



