STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODELING
STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODEL FOR HYPOTHESIS TESTING OF LATENT VARIABLES
In market research, Structural Equation Modeling is used to inspect causal relationships between variables. The objective of such a causal analysis is to investigate hypothetical structures of correlations and influences. As with regression analysis, the analysis looks for the amount and direction of influence of one or more so-called exogenous variables on one or more endogenous variables.
OBSERVABLE VARIABLES AS INDICATORS OF UNOBSERVABLE LATENT VARIABLES
As with factor analysis, the assumption is made that the attribute of real interest cannot be observed directly, but rather that it “latently” represents the basis for the observed behavior, opinion or attitude expressed by the respondent. These latter observations serve as indicators for the level of the underlying basic attributes.
This path analysis is initially based around a hypothesis stating which attributes are influenced by which variables. In this manner, complex covariance structures can be set up, whereby attributes can simultaneously be independent (influencing) and dependent (influenced). The path analysis checks this hypothesis by measuring the degree of the influences and determining the degree of information conveyed by such a modeling.
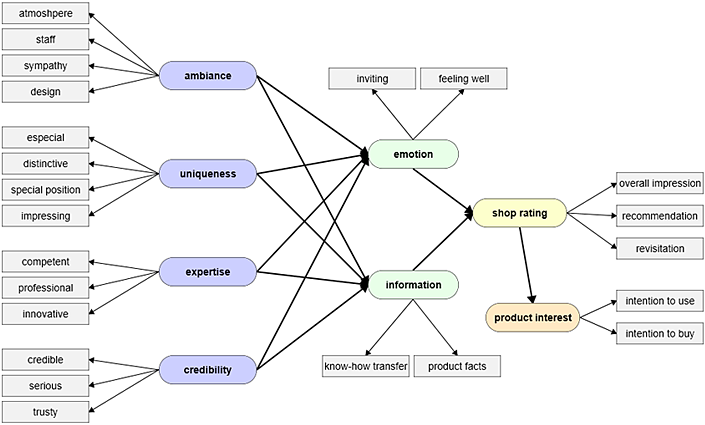
Structural equation model: Example of a causal model – Explanation of a shop rating and the resulting level of product interest
CAREFUL THEORY-DRIVEN MODELING NECESSARY
Path analysis cannot detect an improperly assumed direction of influence. The direction of the influence, or in other words, the question of whether feature A influences feature B or vice versa, must be established through preliminary theoretical consideration.
In order to be able to interpret the coefficients properly, the influencing variables of an endogenous variable should be as mutually independent of one another as possible.
BUILD YOUR OWN STRUCTURAL EQUATION MODEL WITH THE RALV TOOL
Implement with the ADABOX tool RALV (Relationships Among Latent Variables) your own stable and distortion-free causal analysis (structural equation model). RALV enables to play through many model variants quickly and securely without long familiarization or specialized methodological knowledge. Includes orthogonalization as an effective solution for the avoidance of distortions in estimated path coefficients due to multicollinearity.


